Difference between revisions of "Policy"
m (→Policy types) |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
There are currently 14 different policy types. Each policy is targeted to monitor a different aspect of a server. | There are currently 14 different policy types. Each policy is targeted to monitor a different aspect of a server. | ||
| − | # '''[[Command execution policy| | + | # '''[[Command execution policy|Policy:Command_Execution_Policy_Page]]''' runs an executable or script on a server and returns the result |
# '''[[Disk Filesystem policy|Disk / Filesystem]]''' monitors the used space and free space for a file system | # '''[[Disk Filesystem policy|Disk / Filesystem]]''' monitors the used space and free space for a file system | ||
# '''[[Event policy|Event]]''' intercepts an event sent using veloopti-event.exe on the agent and inspect it for a match | # '''[[Event policy|Event]]''' intercepts an event sent using veloopti-event.exe on the agent and inspect it for a match | ||
Revision as of 20:21, 14 February 2021
Home > An Overview > Concepts > Policy
1 Overview
A policy is an instructions for the monitoring of a server for an event that could lead to loss of, or disruption to, an organisation's operations, services or functions. The server should have a Veloopti agent running on it. Policies are deployed to a server that then run on a predefined schedule. This can be anything from once per minute to once per year.
After entering an application use the breadcrumb navigator to select the policies selection to see either a list of policies or the policy groups that are contained in the application. Use the
Policies are created and edited in an application. A policy is represented in Veloopti by the policy icon ![]()
A policy is unique to an application and may only be deployed to servers that reside in the application. In order for a policy to be deployed it must be inside a policy group and the policy group must then be linked to a node group that contains the node(s).
2 Policy types
There are currently 14 different policy types. Each policy is targeted to monitor a different aspect of a server.
- Policy:Command_Execution_Policy_Page runs an executable or script on a server and returns the result
- Disk / Filesystem monitors the used space and free space for a file system
- Event intercepts an event sent using veloopti-event.exe on the agent and inspect it for a match
- HTTP response monitors a webpage for key performance metrics
- Log file watches a log file for text matches or file size
- Ping response ping a host and inspect the return results
- Port availability watches the local or a remote host for the availability of a port
- Process performance watches a local process for key metrics
- Service status watches a local service for service state changes
- SNMP policy polls a SNMP device
- SNMP Trap recipient inspects a received SNMP trap
- Veloopti agent health monitors a Veloopti agent to see whether it is connected or not
- Windows performance library inspects the Windows Performance Library and returns the result
- CI Metric thresholds evaluates against metrics that are collected in the OS Application
3 Deploying a policy to a server
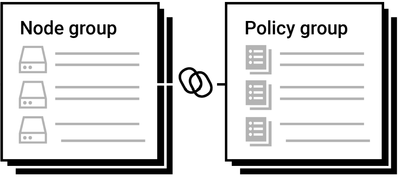
Policies are deployed to a server by adding it to a policy group. The policy group must also be linked to a node group that contains the server that the policy is to be deployed to.
One or more policies can be added to a policy group. A policy in a policy group is a member of the group. In order for the policies in the policy group to be deployed to the nodes in a node group the policy group must be linked to the node group. A policy group can be linked to one or more node groups. All nodes in the node group that have a policy group linked to it can have the policies deployed to them.
A policy group is located in an application and is not able to be linked to a node group outside of the application. A policy cannot be directly deployed to a node.